Monolithic Applications to Micro Services Migration
DevOps & Solution Architecture
AWS CodePipeline
AWS CloudTrail
AWS CloudFormation
Microservice
Php
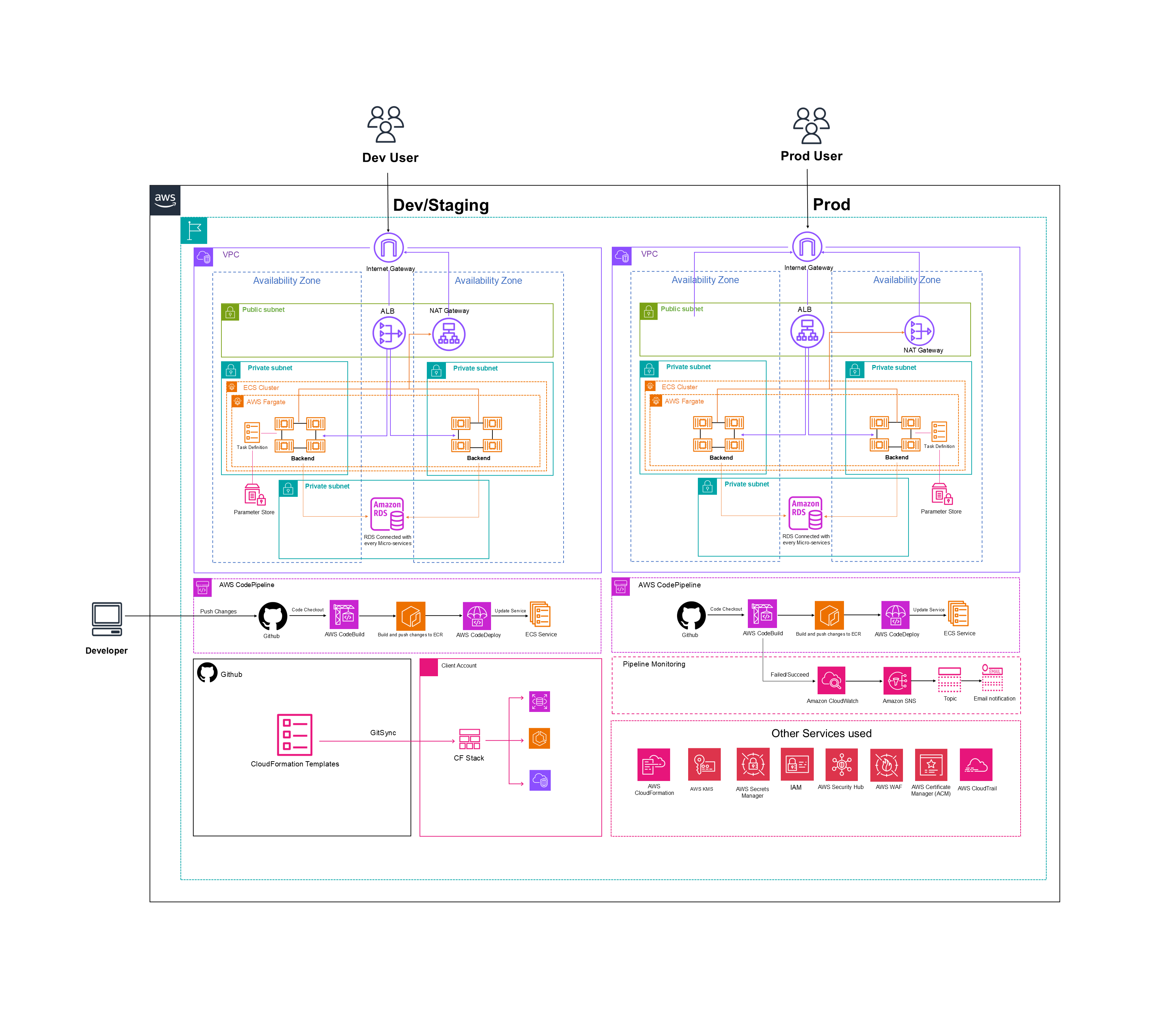
Executive Summary
Moneytos, a global payments company, was struggling with a monolithic application that limited scalability, slowed updates, and caused frequent downtime during peak traffic periods. The lack of Infrastructure as Code (IaC) further complicated operations, as infrastructure changes were manual, error-prone, and time-consuming.
GoCloud partnered with Moneytos to transform its monolithic system into a cloud-native microservices architecture powered by Amazon ECS, AWS Lambda, RDS, and DynamoDB, with automated deployments via CI/CD pipelines and AWS CloudFormation. The modernization improved agility, resilience, scalability, and cost optimization, allowing Moneytos to scale seamlessly during peak traffic while reducing downtime and operational risks.
Customer Challenges
Moneytos faced multiple critical challenges with its legacy setup:
- Monolithic Architecture
- A single codebase slowed updates and made maintenance complex.
- Scalability Issues
- The monolithic application was not designed for horizontal scaling, limiting its ability to handle increased load.
- Downtime During Peak Traffic
- Frequent outages due to single points of failure resulted in lost revenue during high-demand periods.
- Manual Infrastructure Management
- Without CloudFormation or Infrastructure as Code, infrastructure provisioning and updates were manual, error-prone, and hard to replicate across environments.
Requirements
Scalability:
- Scalability: Scale individual components independently based on demand.
- Resilience: Minimize downtime and improve fault tolerance to handle failures effectively.
- Agility: Enable faster and more frequent updates without risking overall system stability.
- Governance & Automation: Standardize infrastructure deployment through Infrastructure as Code.
GoCloud’s Solution
GoCloud proposed and implemented a microservices-based architecture with Infrastructure as Code (IaC) to replace the legacy monolithic setup.
- VPC (Virtual Private Cloud): Isolated network environment
- Subnets: Public and private segmentation of resources
- Internet Gateway & NAT Gateway: Controlled inbound/outbound internet access
- Security Groups & NACLs: Fine-grained traffic control
- CloudWatch & CloudTrail: Monitoring, logging, and auditing
- AWS Config: Continuous compliance enforcement
- Amazon GuardDuty: Automated threat detection
- AWS CloudFormation: Infrastructure as Code for consistent, repeatable deployments
- Amazon ECS (Fargate): Deploy and manage containerized services
- AWS Lambda: Event-driven, serverless services for dynamic workloads
- Amazon RDS (Multi-AZ) & DynamoDB: Reliable relational and NoSQL data storage
- Amazon S3 + CloudFront: Static asset storage and global delivery
- AWS API Gateway: Centralized routing and communication across services
- CI/CD Pipeline (CodePipeline + CodeBuild): Automated build, test, and deployment
Solution Implementation
- Application Review
- Identified monolithic components suitable for decoupling into microservices.
- Containerization
- Used Docker to containerize services for ECS deployment.
- Microservices Design
- Split core functionalities into independent microservices (frontend, backend, payment engine, etc.).
- API Gateway Setup
- Configured API Gateway for secure inter-service communication.
- CI/CD Automation
- Automated deployment pipelines with CodePipeline and CodeBuild integrated with GitHub.
- CloudFormation Templates
- Provisioned VPC, ECS clusters, RDS, DynamoDB, and networking via CloudFormation for consistent, auditable deployments.
- Deployment
- Deployed services on ECS Fargate, with RDS Multi-AZ for resilience and DynamoDB for high-performance NoSQL workloads.
Benefits
Agility
Enabled faster updates and deployments through microservices and CI/CD pipelines.
Resilience
Reduced downtime with Multi-AZ RDS, fault-tolerant ECS, and serverless Lambda functions.
Scalability
Independent microservice scaling ensured smooth handling of peak traffic.
Cost Optimization
Serverless and containerized infrastructure optimized costs by scaling on demand.
Governance & Consistency
CloudFormation ensured repeatable, auditable, and compliant infrastructure deployments.